October 3, 2024
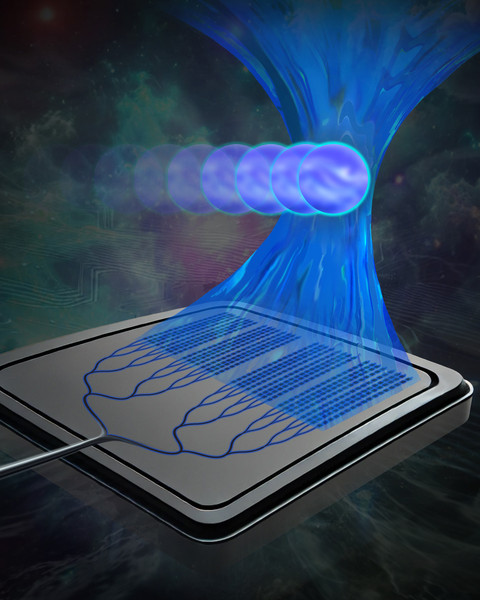
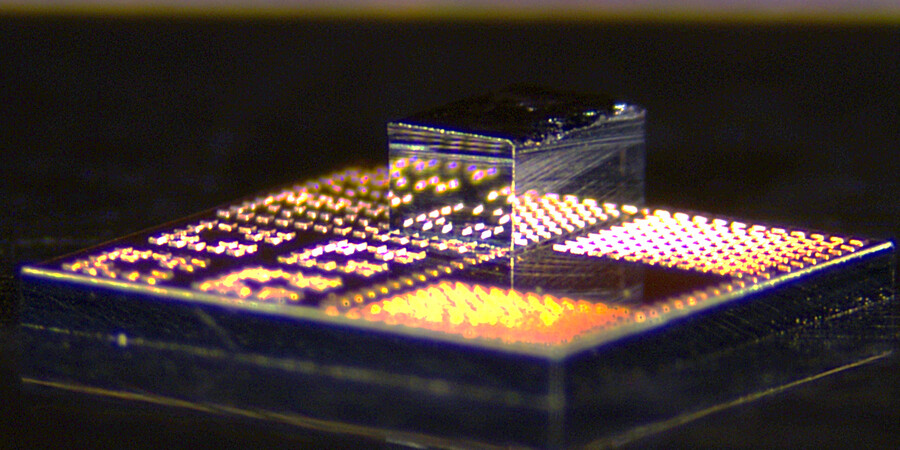
Small enough to fit in the palm of your hand, the device uses a beam of light emitted by a silicon-photonics chip to manipulate particles millimeters away from the chip surface. The light can penetrate the glass cover slips that protect samples used in biological experiments, enabling cells to remain in a sterile environment.
Traditional optical tweezers, which trap and manipulate particles using light, usually require bulky microscope setups, but chip-based optical tweezers could offer a more compact, mass manufacturable, broadly accessible, and high-throughput solution for optical manipulation in biological experiments.
However, other similar integrated optical tweezers can only capture and manipulate cells that are very close to or directly on the chip surface. This contaminates the chip and can stress the cells, limiting compatibility with standard biological experiments.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
New 3D Chips could Make Electronics Faster and more Energy-Efficient
Adam Zewe | MIT News
The low-cost, scalable technology can seamlessly integrate high-speed gallium nitride transistors onto a standard silicon chip.
Anantha Chandrakasan Named MIT Provost
Kathy Wren | MIT News
A faculty member since 1994, Chandrakasan has also served as dean of engineering and MIT’s inaugural chief innovation and strategy officer, among other roles.
Photonic Processor could Streamline 6G Wireless Signal Processing
Adam Zewe | MIT News
By performing deep learning at the speed of light, this chip could give edge devices new capabilities for real-time data analysis.