Adam Zewe | MIT News Office
October 20, 2022
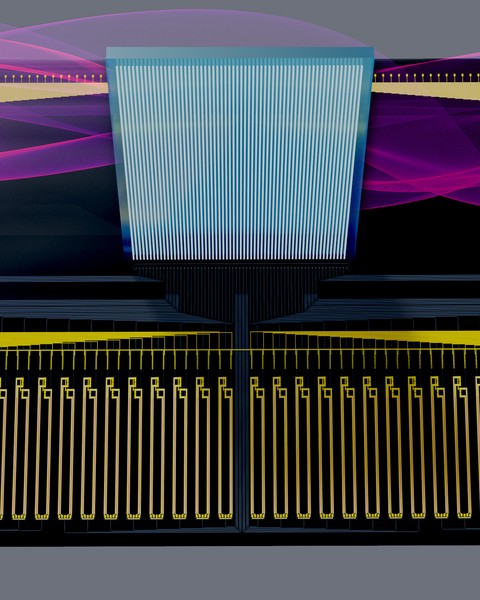
Ask a smart home device for the weather forecast, and it takes several seconds for the device to respond. One reason this latency occurs is because connected devices don’t have enough memory or power to store and run the enormous machine-learning models needed for the device to understand what a user is asking of it. The model is stored in a data center that may be hundreds of miles away, where the answer is computed and sent to the device.
MIT researchers have created a new method for computing directly on these devices, which drastically reduces this latency. Their technique shifts the memory-intensive steps of running a machine-learning model to a central server where components of the model are encoded onto light waves.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
New Method Could Increase LLM Training Efficiency
Adam Zewe | MIT News
By leveraging idle computing time, researchers can double the speed of model training while preserving accuracy.
What Makes a Good Proton Conductor?
Zach Winn | MIT News
MIT researchers found a way to predict how efficiently materials can transport protons in clean energy devices and other advanced technologies.
New Transmitter could Make Wireless Devices more Energy-Efficient
Adam Zewe | MIT News
The flexible chip could boost the performance of current electronics and meet the more stringent efficiency requirements of future 6G technologies.