Jennifer Chu | MIT News Office
February 1, 2023
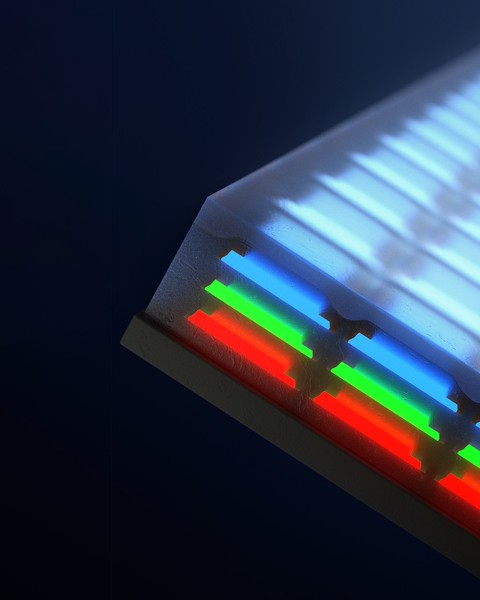
Take apart your laptop screen, and at its heart you’ll find a plate patterned with pixels of red, green, and blue LEDs, arranged end to end like a meticulous Lite Brite display. When electrically powered, the LEDs together can produce every shade in the rainbow to generate full-color displays. Over the years, the size of individual pixels has shrunk, enabling many more of them to be packed into devices to produce sharper, higher-resolution digital displays.
But much like computer transistors, LEDs are reaching a limit to how small they can be while also performing effectively. This limit is especially noticeable in close-range displays such as augmented and virtual reality devices, where limited pixel density results in a “screen door effect” such that users perceive stripes in the space between pixels.
Now, MIT engineers have developed a new way to make sharper, defect-free displays. Instead of replacing red, green, and blue light-emitting diodes side by side in a horizontal patchwork, the team has invented a way to stack the diodes to create vertical, multicolored pixels.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
What Makes a Good Proton Conductor?
Zach Winn | MIT News
MIT researchers found a way to predict how efficiently materials can transport protons in clean energy devices and other advanced technologies.
New Materials Could Boost the Energy Efficiency of Microelectronics
Adam Zewe | MIT News
By stacking multiple active components based on new materials on the back end of a computer chip, this new approach reduces the amount of energy wasted during computation.
MIT Physicists Observe Key Evidence of Unconventional Superconductivity in Magic-angle Graphene
The findings could open a route to new forms of higher-temperature superconductors.
Jennifer Chu | MIT News