David L. Chandler | MIT News Office
March 8, 2022
A method for stabilizing the interfaces in solid-state lithium-ion batteries opens new possibilities.
In the endless quest to pack more energy into batteries without increasing their weight or volume, one especially promising technology is the solid-state battery. In these batteries, the usual liquid electrolyte that carries charges back and forth between the electrodes is replaced with a solid electrolyte layer. Such batteries could potentially not only deliver twice as much energy for their size, they also could virtually eliminate the fire hazard associated with today’s lithium-ion batteries.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
Tomás Palacios appointed Director of ISN
Office of the Vice President for Research
As director, Tomás will lead ISN’s research mission and build communities within MIT and with external partners.
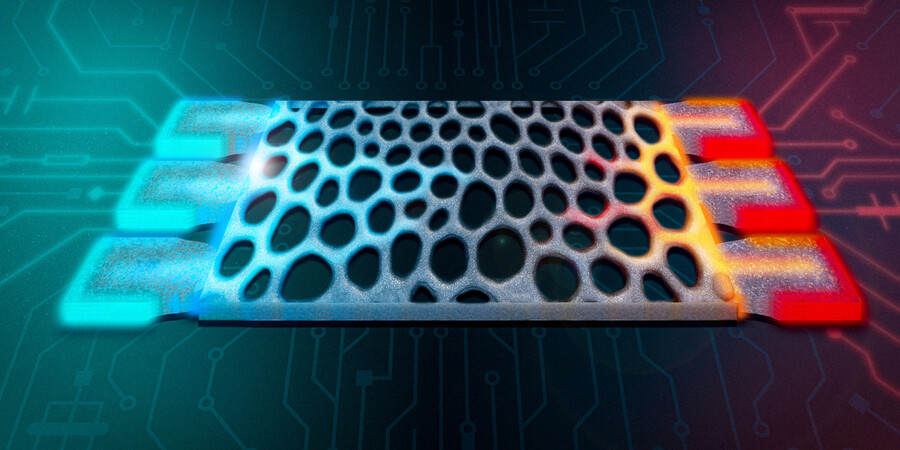
MIT Engineers Design Structures that Compute with Heat
Adam Zewe | MIT News
By leveraging excess heat instead of electricity, microscopic silicon structures could enable more energy-efficient thermal sensing and signal processing.
Pablo Jarillo-Herrero wins BBVA Foundation Frontiers of Knowledge Award
MIT physicist shares award for influential work on “magic-angle” graphene.
Materials Research Laboratory