July 16, 2024
It is estimated that about 70 percent of the energy generated worldwide ends up as waste heat.
If scientists could better predict how heat moves through semiconductors and insulators, they could design more efficient power generation systems. However, the thermal properties of materials can be exceedingly difficult to model.
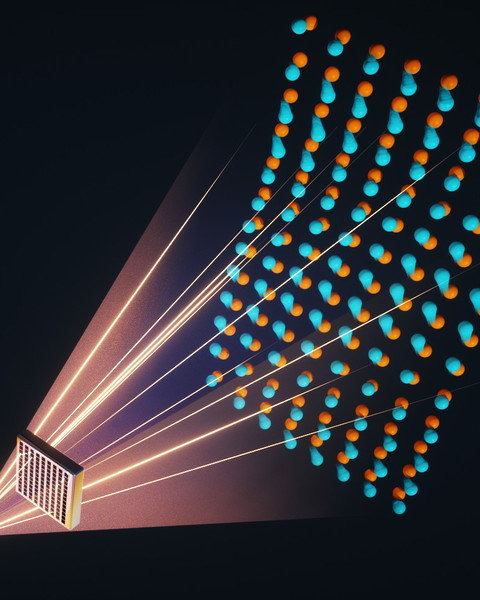
The trouble comes from phonons, which are subatomic particles that carry heat. Some of a material’s thermal properties depend on a measurement called the phonon dispersion relation, which can be incredibly hard to obtain, let alone utilize in the design of a system.
A team of researchers from MIT and elsewhere tackled this challenge by rethinking the problem from the ground up. The result of their work is a new machine-learning framework that can predict phonon dispersion relations up to 1,000 times faster than other AI-based techniques, with comparable or even better accuracy. Compared to more traditional, non-AI-based approaches, it could be 1 million times faster.
Complete article from MIT News.
Explore
What Makes a Good Proton Conductor?
Zach Winn | MIT News
MIT researchers found a way to predict how efficiently materials can transport protons in clean energy devices and other advanced technologies.
New Materials Could Boost the Energy Efficiency of Microelectronics
Adam Zewe | MIT News
By stacking multiple active components based on new materials on the back end of a computer chip, this new approach reduces the amount of energy wasted during computation.
MIT Physicists Observe Key Evidence of Unconventional Superconductivity in Magic-angle Graphene
The findings could open a route to new forms of higher-temperature superconductors.
Jennifer Chu | MIT News